A slew of new laws and regulations that will affect California businesses are taking effect for 2023.
Last year was a busy one, with ground-breaking new laws on employee pay disclosures, a law prohibiting discrimination against cannabis-using employees and another expanding the circumstances when employees can take leave to care for a loved one. The following are the top 10 laws and regulations that employers in the Golden State need to stay on top of.
1. Pay disclosure
This sweeping law in part requires more disclosure of pay information by employers. Under current law, employers are required to provide the pay scale for a position upon reasonable request by a job applicant. SB 1162 goes a step further by:
- Requiring employers, upon request by a current employee, to provide the pay scale of the position they are employed in.
- Requiring employers with 15 or more workers to include pay scale in any job postings for open positions.
- Requiring employers to maintain records of job titles and wage rate history for each employee while employed for the company, as well as three years after their employment ceases.
Note: The law defines “pay scale” as the salary or hourly wage range that the employer “reasonably expects” to pay for the position. Penalties range from $100 to $10,000 per violation. This law took effect Jan. 1, 2023.
2. State of emergency and staff
This new law, SB 1044, bars an employer, in the event of a state of emergency or emergency condition, from taking or threatening adverse action against workers who refuse to report to, or leave, a workplace because they feel unsafe. “Emergency condition” is defined as:
- Conditions of disaster or extreme peril to the safety of persons or property caused by natural forces or a criminal act.
- An order to evacuate a workplace, worksite or worker’s home, or the school of a worker’s child due to a natural disaster or a criminal act.
SB 1044 also bars employers from preventing employees from using their mobile phones to seek emergency assistance, assess the safety of the situation or communicate with another person to confirm their safety. The law, which took effect Jan. 1, 2023, does not cover first responders and health care workers.
3. Cannabis use and discrimination
This law bars employers from discriminating in hiring, termination or other conditions of employment based on employees using cannabis while off duty. The bill’s author says the legislation is necessary because THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the active ingredient in marijuana, can stay in a person’s system after they are no longer impaired. As a result, drug testing may detect THC in an employee’s system even if they used it weeks earlier and it is having no effect on their job performance. AB 2188 does not require employers to permit employees to be high while working. The bill would exempt construction trade employees and would not preempt state or federal laws that require employees to submit to drug testing. This law takes effect Jan. 1, 2024.
4. Leaves of absence
The California Family Rights Act and the state’s paid sick leave law allow employees to take leave to care for a family member, defined as a spouse, registered domestic partner, child, parent, parent-in-law, grandparent, grandchild or sibling. The definition has been expanded to include “any individual related by blood or whose association with the employee is equivalent of a family relationship.”
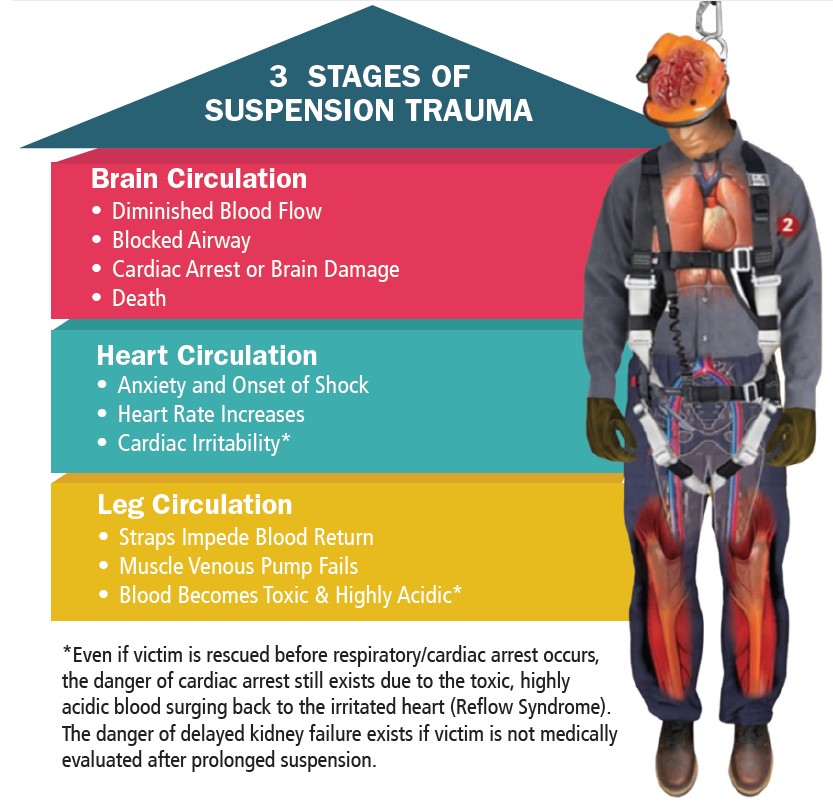
5. Contractor workers’ comp
Starting July 1, the following contractors must carry workers’ compensation coverage regardless of if they have employees or not:
- Concrete (C-8 license)
- Heating and air conditioning (C-20)
- Asbestos abatement (C-22), and
- Tree service (D-49).
Starting Jan. 1, 2026, all licensed contractors must have coverage.
6. OSHA citation postings
Under current law, employers that receive citations and orders from OSHA are required to post them in or near the place the violation occurred, in order to warn employees about a potential hazard. Starting Jan. 1, 2023, they must post the notice not only in English, but also: Spanish, Chinese (Cantonese, Mandarin), Vietnamese, Tagalog, Korean, Armenian and Punjabi.
7. Permanent COVID standard
Cal/OSHA has a permanent COVID-19 prevention standard that will sunset in 2024. The new standard, which replaces the temporary emergency standard the agency had implemented, should provide more certainty for prevention procedures and practices. Here are the main takeaways:
- Employers are no longer required to pay employees while they are excluded from work due to COVID-19, or to screen employees daily.
- Employers must still notify and provide paid testing to employees who had a close contact in the workplace.
- Employers can now incorporate written COVID-19 procedures into their Injury and Illness Prevention Programs.
8. CalSavers expanded
SB 1126 requires any person or entity with at least one employee to either provide them with access to a retirement program like a 401(k) plan or enroll them in the state-run CalSavers program. Prior to this new law only companies with five or more employees that do not offer a retirement plan are required to enroll their workers in CalSavers.
9. Bereavement leave
Employers with five or more workers are required to provide up to five days of bereavement leave upon the death of a family member, under a new law starting in 2023. This leave may be unpaid, but the law allows workers to use existing paid leave available to them, such as accrued vacation days, paid time off or sick leave. Employers are authorized to require documentation to support the request for leave.
10. PFL wage replacement
This law was passed last year but does not take effect until 2025. Existing California law allows employees to apply for Paid Family Leave and State Disability Insurance, both of which provide partial wage replacement benefits when employees take time off work for various reasons under the California Family Rights Act. Starting in 2025, low-wage earners (those who earn up to 70% of the state average quarterly wage) will be eligible for a higher percentage of their regular wages under the state’s PFL and SDI benefit programs.