Jan 2025 – Salt Typhoon – A New Cyber Threat Businesses Can’t Ignore

AN ALLEGEDLY Chinese state-sponsored hacker campaign dubbed “Salt Typhoon” has infiltrated major cell phone providers, including AT&T and Verizon, potentially exposing your company’s communications to threat actors.
The attack has been described as the most significant telecommunications hack in U.S. history. While the breach is alarming for individuals, the implications for businesses are profound and demand immediate attention.
What is Salt Typhoon?
Salt Typhoon is a sophisticated cyber-espionage operation allegedly orchestrated by the Chinese government.
The campaign has targeted vulnerabilities in telecom providers’ infrastructure to access text messages, monitor communications, and extract sensitive metadata.
The ongoing breach has affected at least eight major U.S. telecom companies and poses a severe threat to national security and corporate privacy.

Government warning
In response to Salt Typhoon, the U.S. government recommended using end-to-end encrypted communication platforms.
Unlike standard text messaging or phone calls, end-to-end encryption ensures that only the sender and recipient can read the messages.
Protecting your firm
Some steps businesses can take include:
• Shifting internal and external communications to end-toend encrypted platforms such as Signal or WhatsApp, or enterprise solutions with encryption features.
• Avoiding using text-based, one-time passwords for authentication; instead, deploy hardware security keys or app-based authenticators.
• Updating systems regularly: Ensure all devices and software are updated to patch known vulnerabilities.
• Conducting regular training to educate employees about phishing, secure communications and device management.
• Limiting data access: Implement least-privilege access controls to restrict sensitive data to only those who need it.
• Regularly auditing your infrastructure for vulnerabilities.

April 2024 – Protecting Your Data – Deepfake Technology Used to Fool Employees

THE NEWEST cyber and financial fraud threat facing businesses is deepfake technology, which criminals are using to extract money from unsuspecting accounts payable personnel.
A finance worker at a multinational company in Hong Kong was duped into transferring $25 million to criminals who had used deepfake technology to pose as the business’s chief financial officer during a video conference call, according to local police.
A deepfake is an artificial image or video generated by a special kind of machine learning called “deep” learning. The creations have grown increasingly sophisticated and harder to detect.
How it happened
The worker received an e-mail from what he thought was the company CFO, inviting him to attend a teleconference with him, other company executives, and staff, according to Hong Kong police. The digitally recreated version of the CFO then ordered money transfers during the video conference call.
Based on instructions the employee got during that call, they transferred 200 million Hong Kong dollars ($25.6 million) to various Hong Kong bank accounts in a series of transactions.
The employee did not interact with the deepfakes during the video conference, and he later told police that others on the call looked and sounded like people he knew in the organization.
In fact, all of the other people on the call were fakes of real people in the company. The criminals had used deepfake tech to alter publicly available video and footage found online to create convincing digital versions of the others in the meeting.
Police said that the case was one of several recent incidents in which criminals had used deepfake technology to change publicly available video and other footage to steal from people and companies.
Warning to US businesses
This type of attack is essentially an extension of the wire transfer fraud, a threat that’s been growing in recent years.
These scams usually start with e-mails or even phone calls from scammers posing as someone higher up in an organization, a client or vendor. The end goal is to convince an employee with access to the company’s payment systems to transfer funds to the criminals.
Deepfake technology adds a dangerous new arrow to wiretransfer fraud criminals’ quivers, making the scam even easier to fall for.
To avoid being victimized, the law firm of Fischer Phillips recommended in a November 2023 blog that businesses:
Provide deepfake training to staff. You should already be training and providing refresher meetings on preventing cyber attacks of all sorts. Consider educating them about the dangers of deepfakes and provide the Hong Kong case as an example. Cover ways to spot deepfakes, including:
• Blurry details,
• Irregular lighting,
• Unnatural eye and facial movements,
• Mismatched audio, and
• Absence of emotion.
Urge staff to be suspicious. Your employees should be able to comfortably question the legitimacy of information and be urged to report suspicious activity.
Use strong authentication protocols. Put in place robust measures — like multi-factor authentication and similar tools — for accessing sensitive information and systems.
Insurance coverage
If your organization has a cyber insurance policy, it might cover a wire transfer fraud loss. The coverage provided by cyber insurance can vary significantly between insurance companies and policies. Some cyber policies may explicitly cover wire fraud, while others require additional endorsements or riders to provide adequate protection.
A commercial crime policy will cover losses resulting from the use of a computer to fraudulently transfer funds from inside the business premises or the insured’s bank to an outside party.
However, policies may only offer coverage if an employee was fraudulently involved in the wire transfer fraud. This type of funds transfer fraud is basically the only computer-related coverage that a crime policy offers.
January 2023 – Ransomware Fallout – Firms That Pay Ransom Often Hit Again

A new report found that one-third of companies who are hit with ransomware and pay the hackers to unlock their systems, are often likely to be targeted a second time.
And after they pay, they are often faced with significant consequences, including system rebuilding costs, their data still being leaked and financial consequences, according to the “2022 Cyber Readiness Report” by Hiscox. The eye-opening results of the study come as the number of businesses hit by cyber attacks continues growing.
Considering the potential damage to your organization if your systems are compromised in the aftermath of a ransomware attack, even if you have cyber insurance to pay recovery costs, it’s best to take steps to thwart attacks in the first place.
More than ransom
It’s clear that paying a ransom often doesn’t mean the recovery for an affected business will be smooth, according to the report, which covers the poll results of 5,000 organizations.
 The risk
The risk
Nearly half (47%) of firms reported that they had been hit by a cyber attack during the past 12 months, up from 40% in 2021. Of those who were attacked, 17% were ransomware victims.
The median cost of an attack has risen 29% to just under $17,000.
Small firms can no longer expect to fly under the radar as the criminals increasingly have them in their sights.
What you can do
Some firms have little exposure to a cyber attack, particularly if they don’t handle customer data or are not techdriven operations. Each firm has a different exposure level.
For companies that have cyber exposure, protecting their organization requires a multi-pronged approach that includes cyber insurance and strong data security protocols.
Cyber insurance may cover the cost of a paid ransom as well as recovery and rebuilding costs. If your organization has exposure, please give us a call to review your risk and see if cyber insurance is right for your business.
Besides that, Hiscox recommends taking a number of steps to protect against an attack and be able to recover from one faster:
- Keep all of your software up to date to include the installation of all the latest security patches.
- Frequently back up your data on a server that is not hooked up to the cloud.
- Train workers on how to recognize and avoid common social engineering attacks that criminals use to trick them into revealing sensitive information about themselves or their company.
- Teach your staff how to detect potentially dangerous e-mails that try to get them to click on a malicious link that can unleash ransomware or other malware.
April 2022 – Growing Threat – Funds Transfer Fraud Hits Small Firms the Hardest

WHILE RANSOMWARE is making the headlines as the major cyber threat, small and mid-sized businesses are increasingly being targeted by lower fraud that dupes them into wiring criminals funds, according to a new report.
These funds transfer fraud crimes involve hackers gaining access to a firm’s mailbox and extracting payments that go into their accounts. Companies should have in place proper systems safeguards to combat these attacks, and that includes regularly training staff on how to identify these attempts to steal funds.
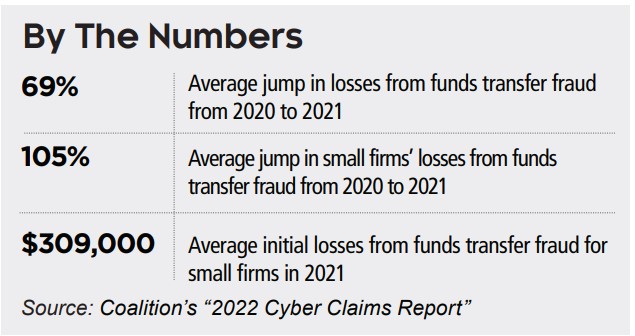
How it works
Criminals will often try to penetrate your servers by sending “spearphishing” e-mails. These messages look like they’re from a trusted sender to trick victims into revealing confidential information. They may also send malicious e-mails in the hope that an employee clicks on a bogus link. The link then releases malicious software that infi ltrates company networks and gains
access to legitimate e-mail threads about billing and invoices.
Once the criminals have access to your business mailbox, they can manipulate your contacts and modify payment instructions. They may also use their access to your systems to send e-mails that appear to come from a known source making a legitimate request.

Insurance options
The best option for coverage is a commercial crime insurance policy. Most of these policies cover acts like:
• Employee dishonesty
• Computer and funds transfer fraud
• Forgery or alteration
• Money and securities theft
• Theft of client’s property.
Some policies may exclude funds transfer fraud, or they may have lower sublimits for such acts. In such cases you may need to get a policy extension to cover the risk. There is also cyber liability insurance, which covers direct losses resulting from cyber crime. But these policies will often exclude coverage for social engineering attacks, which are the kinds that the criminals behind funds transfer fraud use. You may be able to purchase a rider to your cyber liability policy that would cover these crimes.
CYBER SECURITY – Malicious Coronavirus-related E-Mails Spread – April 2020

AS IF BUSINESSES didn’t have enough to worry about, online scammers have started sending out malicious e-mails to organizations about coronavirus that appear to be from business partners or public institutions. The criminals send these to rank and file employees in the hope that at least one of them will click on a link or attachment in the e-mail, which unleashes malware or tries to trick them into wiring money for supplies purportedly to protect the organization’s workers.
The number of malicious e-mails mentioning the coronavirus has increased significantly since the end of January, according to cybersecurity firm Proofpoint Inc. The company noted that this wasn’t the first time they had seen such widespread cyber attacks associated with some type of disaster. But because this is global in nature, it decided to track the new threat. This practice of launching cyber attacks that are centered around global news and outbreaks (like the current COVID-19 coronavirus) isn’t anything new. Cybercriminals have long employed these tactics to take advantage of users’ desires to keep as up to date with any new information as possible or to evoke powerful emotions (like fear) in the hope that their sentiments will get the better of them and they will not pause to check for the legitimacy of these e-mails.
The cybercriminals are using the public’s ignorance about coronavirus, as well as the conflicting claims of how to protect against it, to lure people into clicking on their malicious links or get them to wire money. Because people are afraid, their guards may be down and they may not be as careful about identifying the e-mail as dangerous.
Some real-life examples
• Japanese workers were targeted in January and February with e-mails that looked like they came from local hospitals. The messages even included legitimate contact information for key personnel. The e-mails were focused on employees of various companies and came in a message that would look like it’s a reply to something or a warning that people are getting from the government. But when they clicked, it was malware. E-mails were sent to companies in the transportation sector that looked like they came from an employee of the World Health Organization.
They included the WHO logo and instructions about how to monitor crews aboard ships for coronavirus symptoms, and they included an attachment with instructions. This phishing e-mail attack was
intended to lure individuals into providing sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information and passwords.
• Companies in the US and Australia have been receiving malicious e-mails that use a display name of “Dr. Li Wei” and are titled “CORONA-VIRUS AFFECTED COMPANY STAFF.”
What you can do
All that it takes to break into your business is a cleverly worded e-mail message. If scammers can trick one person in your company into clicking on a malicious link, they can gain access
to your data. It’s important to train your staff to identify suspicious e-mails. They should avoid clicking links in e-mails that:
• Are not addressed to them by name, have poor English, or omit personal details that a legitimate sender would include.
• Are from businesses they are not expecting to hear from.
• Ask you to download any files.
• Take you to a landing page or website that does not have the legitimate URL of the company the e-mail is purporting to be sent from.
• Include attachments purportedly with advice for what to do. Do not open them even if they come from relatives or friends.
KEEPING OPERATIONS GOING – Tips for Successful Telecommuting – April 2020

WITH THE current isolation orders for most workers in California, many companies have had to scramble to put systems in place to allow their employees to telecommute. Many businesses are not set up for having employees work from home, and they have legitimate concerns about productivity and communications. But there are steps you can take to make sure that you keep your employees engaged and on task.
1. Make sure they have the right technology
If you don’t already have one, you may want to consider setting up a company VPN so your employees can access their work e-mail and databases. You will also need to decide if you are going
to provide them with a company laptop, and you need to make sure that they have an internet connection that is fast enough to handle their workload. Also provide an infrastructure for them to be able to work together on files. If they are not sensitive company documents, they can use Dropbox or Google Documents, which allow sharing between co-workers.
2. Provide clear instructions
It’s important that you provide clear instructions to remote workers. Some people do not perform well without direct oversight and human interaction. Without that factor, you will need to spell out your expectations and the parameters of the projects they are working on in detail. Make it clear that if they are confused or unsure about any part of the work, they should contact a supervisor for clarification. If you can eliminate misunderstandings, then your workers can be more efficient.
3. Schedule regular check-ins
To hold your employees accountable for being on the clock, schedule calls or virtual meetings at regular intervals. Even instant messaging works. During these meetings they can update their
superiors on their work. This also helps with productivity, since there are consequences for failing to meet expectations and coming to the meeting empty-handed. Their supervisors should be working when they are, so they can be in regular communication.
4. Keep employees engaged
One of the hardest parts of working from home is the feelings of isolation and detachment from colleagues. It’s important that you build in interactive time for your workers. One way to do that is by using a chat program like Slack, Hangouts or WhatsApp (which has a group chat function). For remote workers, these programs are a blessing because they make it easy to keep in touch with their colleagues in and out of the office – and they level the playing field, so to speak, by making distance a non-issue.
5. Cyber protection
With employees working from home, you also increase your cyber risk exposure, especially if they are using a company computer that is tapped into your firm’s database or cloud. Teach them cyber security best practices, such as:
• Not clicking on links in e-mails from unknown senders.
• Making sure their systems have the latest security updates.
• Backing up their data daily.
• Training them on how to detect phishing, ransomware
and malware scams, especially new ones that try to take advantage of people’s fears about COVID-19.
Finding Coverage for the Latest E-mail Scams – INSURANCE ISSUES

As cyber scams and hacker attacks grow, the insurance industry has been frantically trying to keep up in providing appropriate coverage for these events.
Hacks, viruses, ransomware and exposure of sensitive personal information of your customers or employees, and any resulting regulatory implications, are often covered by cyber liability insurance. But what about the recent trend of criminals spoofing a company executive’s e-mail address, posing as them and ordering accounts payable to cut a check and send it to the fraudsters?
Well, two firms suffered similar incidents, but different federal appeals courts issued opposite opinions – one saying that a crime insurance policy covered the event, while the other court said it didn’t.
The fact that two courts came out with two different rulings illustrates how many traditional and even cyber policies are slow to keep up with evolving hi-tech threats to businesses. The devil is always in the details, so read your policies and discuss your concerns with us.
The number of business e-mail compromise scams quadrupled in 2017, and losses averaged $352,000 per business and topped out at $3 million, according to an analysis of insurer Beazley’s clients. The FBI says these schemes are one of the fastest-growing cyber crimes.
Court case one: Covered
Employees of Medidata, a clinical-trial software firm, wired $4.7 million for what they thought was for an acquisition by their employer. They were sent a series of fraudulent e-mails that they thought were from their company president and the firm’s outside lawyer.
The company didn’t have a cyber insurance policy, but it had an executive protection policy, which had a crime section that included coverage for computer fraud, funds-transfer fraud and forgery.
The insurer rejected the claim and the firm sued in federal court. The lower court ruled in favor of the insurer, but
upon appeal the federal appeals court ruled that the policy did in fact cover the loss.
The insurer argued the policy applies to only hacking-type intrusions. The appeals court found that while no hacking occurred, fraudsters inserted spoofing code into firm’s e-mail system, which the court said is part of the computer system. The court held that the insurer must pay under the computer fraud portion of its policy.
Court case two: Not covered
A federal district court found no crime policy coverage after a Michigan tool and die firm wired $800,000 in funds to a fraudster’s account in the belief the account belonged to one of its vendors.
The insurer faulted the company for not verifying the bank account with the vendor. The district court agreed with the insurer that the loss was not a “direct loss” caused by the “use of a computer,” and thus the crime policy did not apply.
The takeaway
Computer fraud is evolving rapidly, so it’s important that you talk to us about the types of fraud that appear in the news. We will work with you to ensure that your coverage is forwardlooking and covering more than just threats from last year. We can also discuss with you how computer fraud coverage interacts with other types of cyber crime policies.






 The risk
The risk





