October 2024 – Proposed Rules Take Aim at ‘Egregious’ Violators

CAL/OSHA is working on new rules that would crack down on and step up enforcement and penalties against California employers that commit “egregious” and “enterprise-wide” workplace safety violations.
To enforce the impending rules, the agency is ramping up the hiring of investigators to identify egregious violators and to refer more employers for criminal prosecution.
The forthcoming rules would impose substantial penalties on companies that have shown a disregard towards California workplace safety regulations and the wellbeing of their employees.
Employers that are cited for egregious violations could be fined up to $158,000 “per instance,” meaning it can be applied for each employee exposed to the violation.
Here’s what’s on tap:
Enterprise-wide violation
Under the proposed rules, a violation is enterprise-wide if an employer has multiple worksites and either of the following is true:
• The employer has a written policy or procedure that violates occupational safety and health regulations; or
• The Division of Occupational Safety and Health has evidence of a pattern or practice of the same violation or violations involving more than one of the employer’s worksites.
Egregious violation
The proposed rules define an egregious violation as a willful violation where the employer has had a previous egregious violation in the past five years. One or more of the following must apply:
• The employer intentionally made no reasonable effort to eliminate a known violation.
• The employer has a history of one or more serious, repeat, or willful violations or more than 20 general or regulatory violations per 100 employees.
• The employer intentionally disregarded its health and safety responsibilities, such as by failing to maintain an Injury and Illness Program, ignoring safety hazards, or refusing to comply with regulations.
• The employer’s conduct amounts to clear bad faith in the performance of their duties to comply with occupational safety and health standards.
• Within the five years preceding a citation for an egregious violation, the employer has committed more than five violations of any Title 8 standard that has become TWO NEW PENALTY finalized.
• The violations resulted in worker fatalities, a worksite catastrophe, or five or more injuries or illnesses. Catastrophe is defined as inpatient hospitalization of three or more workers from a workplace hazard.
• Within the 12 months immediately preceding the underlying violation, 10% of all employees at the cited worksite sustained workplace injuries or illnesses.

The takeaway
The proposed regulations pose the largest risk for companies with multiple locations.
Fines will be adjusted each year to account for inflation. Employers should double down on their workplace safety efforts and ensure that there is buy-in to the program from top management down to supervisors and line workers at all locations.
July 2023 – Cal/OSHA Rule-Making – Indoor Heat Illness Prevention Standard on Tap

Cal OSHA has proposed its long-awaited indoor heat illness prevention standard as increasingly hot summers are affecting workers in indoor spaces like warehouses, production operations,
restaurants and more.
The proposed standard, largely based on the state agency’s outdoor regulations, will require employers whose workplaces at times are at least 82 degrees to have a written Indoor Heat Illness Prevention Plan.
The standard, once it takes effect, will affect employers throughout the state and many will have to take steps and invest in equipment and planning to ensure compliance. The preventative measure to which most employers will likely resort is air-conditioning.
The Standards Board wrote in its proposal, according to the Cal-OSHA Reporter trade publication: “There is likely to be a particular need to reduce temperatures in large warehouses, manufacturing and production facilities, greenhouses, and wholesale and retail distribution centers.”
Other facilities that would likely also need to install HVAC units include restaurant kitchens and dry cleaners. They may also need to improve air circulation in their operations.
Under the proposal, the following regulations apply to a workplace where the indoor temperature exceeds 82 degrees.
Access to drinking water
Employers are required to provide access to potable water that is fresh, suitably cool, and free of charge.
It must be located as close as practicable to the work area, as well as indoor cool-down areas where employees can rest. If an employer doesn’t provide water continuously, it will be required to provide at least one quart per hour per employee per shift.
Employers should encourage frequent water consumption.
Access to cool-down areas
Employers must provide at least one cool-down area during shifts, and grant a cool-down break to staff who ask for one.
Workers taking cool-down breaks shall be monitored and asked to stay in the area if they are experiencing heat illness symptoms. As long as symptoms persist, they may not be ordered back to the work they were doing.
Control measures
Employers can implement a number of measures to protect their workers:
Engineering controls – This can include barriers between heat sources and employees, isolating hot processes from workers, air-conditioning, cooling fans, mist fans, swamp coolers, ventilation, etc.
Administrative controls – This can include limiting exposure by adjusting work procedures, practices, or schedules (working during cooler periods, using work/rest schedules, or reducing the speed of work).
Personal heat-protective equipment – This could include water- and air-cooled garments, cooling vests, and more.
Emergency response procedures
Employers will need to develop and have in place emergency response procedures that workers and supervisors can follow in case they are experiencing heat illness.
Acclimation steps
Employees should be closely observed during heat waves, and new workers must be closely observed during their first 14 days of work to ensure they are acclimating.
Training
Employees and supervisors will need to be trained on:
- Personal risk factors for heat illness.
- Their employer’s procedures for complying with the regulation.
- The importance of frequent water consumption.
- The importance of acclimation.
- Signs and symptoms of heat illness, and first aid or emergency response procedures.
July 2023 – Class Code Changes Okayed by Insurance Dept

If you have staff who work remotely, you’ll want to pay attention to changes that are coming to the workers’ compensation class code you use for them.
Starting Sept. 1, California’s telecommuter class code will finally get its own pure premium rate, that is lower than what’s currently being charged.
Since many people started working remotely after the COVID-19 pandemic began in 2020, the Workers’ Compensation Insurance Rating Bureau created a new telecommuter class code (8871) and tethered its pure premium advisory rate to the 8810 clerical classification for easier administration.
Now, under the Rating Bureau’s workers’ compensation regulatory filing which was adopted by the California Department of Insurance on May 25, code 8871 will receive its own rate, separate from the clerical rate. In fact, the new telecommuter rate will be 25% lower than the clerical rate due to the former’s lower losses and higher average payroll.
If you have remote workers, you’ll want to ensure they are in the telecommuter class code to enjoy the lower premium.
New X-Mod threshold
The approval of the filing also increases the workers’ comp premium threshold for experience rating (being eligible for an X-Mod) to $10,200 from $9,200 to account for wage inflation.

Restaurant classification split
Other changes include splitting the 9079 restaurant classification into six new codes (see box below), effective Sept. 1, 2024.
While there will be six codes, they will still be combined for rate-making purposes until the Rating Bureau collects a few years of data from the new codes, so that it can set individual rates
for each of them.

April 2023 – Workplace Safety – Construction Falls and the Perils of Suspension Trauma
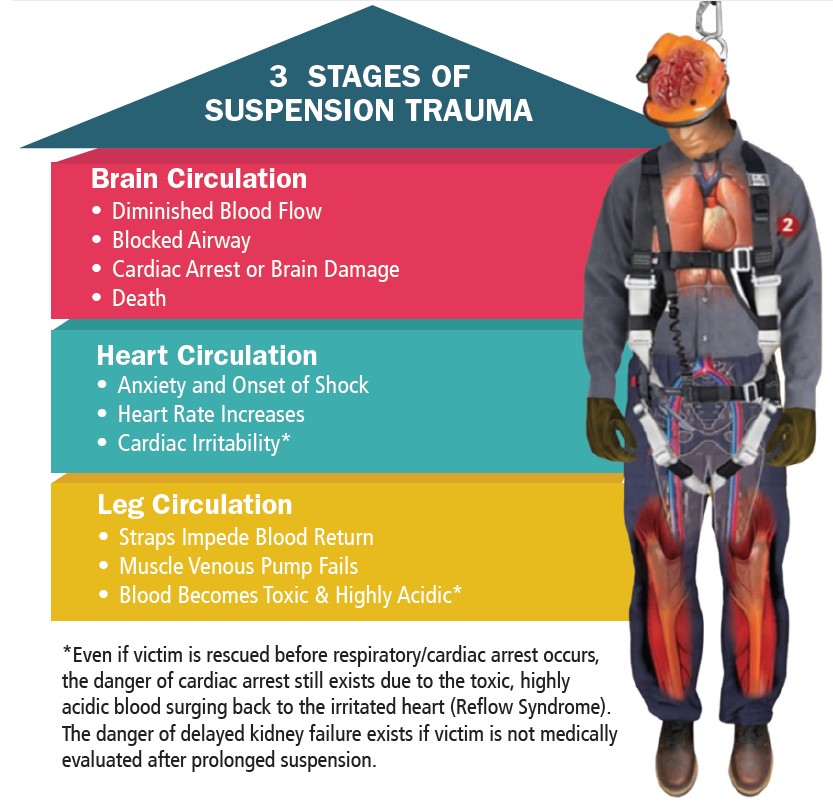
ONE OF THE most common construction industry accidents is falls from heights, which is why it’s crucial that you have in place fall protection systems for your workers.
One of the best ways to prevent injuries and death from falls is by using a fall-arrest system. But while these systems can save lives, they can cause suspension trauma if the worker is not rescued and brought to ground level as soon as possible and is instead left suspended in an upright position, with their legs dangling.
Because the worker is suspended in an upright position with their legs hanging, blood begins to accumulate in the legs.
This is commonly called venous pooling (the accumulation of too much blood in the veins), which reduces the flow of oxygenated blood to the heart and brain.
Remaining in this position for a long time can cause the worker to pass out and the longer they hang in place, the more it can result in serious health problems – and even death.

How to avoid suspension trauma Safe, prompt rescue is the key to preventing suspension trauma. The sooner a worker can be rescued, the less likely they are to endure such trauma.
During the rescue, care should be taken to slowly put the victim back on the ground. Try to avoid suddenly letting them into a horizontal position, which can cause deoxygenated blood to flow back into the body (reflow syndrome) and cause damage to the brain and other organs – and even cause the heart to stop.
Suspended workers awaiting rescue can take some action to guard against injury, including:
- Adopting a sitting position, if possible.
- Moving into a horizontal position as much as possible.
- Using their legs to push off from a hard surface, keeping the muscles active.
- Pumping legs frequently to maintain blood flow and prevent venous pooling.
One of the primary ways to slow the progression of suspension trauma is to stand up. When standing, the leg muscles must contract to provide support and maintain balance and these actions also put pressure on the veins. This pressure, along with a series of one-way valves in the veins, helps blood get to the heart and reduces the amount of blood pooling in the legs.
Workers can “stand” by using the trauma-relief straps that are attached in pouches on the side of the fall-arrest harness. When suspended, the worker can deploy the trauma-relief straps, which provide a loop that they can put their feet into and press against to simulate standing up.


April 2022 – Risk Management – Don’t Let a Subcontractor Derail Your Safety Efforts

ONE OF the biggest challenges construction businesses face is preventing subcontractors’ and suppliers’ poor or non-existent safety practices from denting their own safety program.
While you may consider a number of factors when vetting a new subcontractor or vendor, one area that is often overlooked is their workplace safety practices.
This mistake can cost you dearly if one of their workers causes an incident at your worksite. In addition to an injury to one of your own employees, you could get a visit from an Occupational Safety and Health Administration inspector.
The National Safety Council’s Campbell Institute recently conducted a study of organizations with excellent safety records to identify the best practices for subcontractor and vendor safety.
As part of the study it identified five steps during a contractor or vendor relationship when it’s incumbent on a hiring company to evaluate the workplace safety habits of their business partners.
Prequalification
The institute recommends looking at more than just a company’s experience modifi cation rate. It says safety-minded fi rms assess subcontractors in multiple areas, such as their total recordable incident rate, fatality rate, days away from work for injured workers, restricted or transferred rate, and other OSHA recordables for the last three years.
Many firms also ask for environmental reports, written safety programs, permits, licenses, and continuous improvement programs.
Pre-job task and risk assessment
Before a subcontractor begins work, institute members recommend having a method for evaluating the risk of the work that is to be performed. Doing this can help you understand the scope of the work and give you a chance to put into place a new written safety program if the risk is deemed high.
Most importantly, subcontractors should be required to adhere to the same safety standards as your company.
Training and orientation
You should require safety orientation and skills training for subcontractors before they step onto your jobsite. Also, if they are doing highly specifi c work, you should ensure they have any required permits or special training. Some of the jobs that fit into that category are confi ned-space entry, electrical work, hot work, energy control, forklifts, and elevated work.
Job monitoring
Many safety-minded companies monitor work with daily checklists, pre-shift tailgate or safety meetings and weekly walkthrough inspections. Some of the companies surveyed for the study also require contract employees to submit a certain amount of safety observations and utilize mobile applications to report non-compliance or unsafe conditions. Also, you need to keep up-to-date incident logs, as this is crucial to monitoring subcontractor safety during a project.
Post-job evaluation
Conduct a post-job evaluation. During this phase look at safety, customer service and the quality of the fi nished work, and use those factors in determining the subcontractor’s eligibility for future contracts.
October 2021 – WORKPLACE SAFETY- Permanent COVID-19 Standard Coming Soon

CAL/OSHA has taken the first step towards creating a semi-permanent COVID-19 standard to replace the emergency temporary standard that currently governs workplace coronavirus prevention measures in the state.
On Sept. 17, Cal/OSHA released a discussion draft for permanent COVID-19 regulations to give stakeholders the chance to comment on it before it starts work on writing the regs. Even though they are “permanent,” the rules would be subject to renewal after two years from the effective date or they would expire if the threat has receded by that time.
Elements of the draft standard
Here’s what the draft standard would do:
Follow CDPH rules – Required that employers follow California Department of Public Health COVID-19 prevention orders.
Masks for unvaxxed staff – Unvaccinated staff must wear masks. Employers must provide masks when the CDPH requires them.
Outbreak rules – During an outbreak in the workplace, all staff would be required to wear face coverings regardless of vaccination status. Employers would need to provide respirators during major outbreaks to all employees.
No COVID-19 Prevention Plan – Employers would not need to have a COVID-19 Prevention Plan, as required in the temporary emergency standard. Instead, they would be required to address COVID-19 prevention strategies in their Injury and Illness Prevention Plan.
Masks for at-risk staff – Require employers to provide N95 respirators to employees who have been identified by a doctor as being at increased risk of severe illness from COVID-19, regardless of their vaccination status.
‘Fully vaccinated’ defined – Define a “fully vaccinated employee” to mean that the employer has a copy of their vaccination record that includes the vaccine maker and date of the last dose.
Retaining records – Require employers to keep COVID-19 vaccination records for two years after the period requiring them to keep the records ends. That means if the rule sunsets in a few years, employers would be required to keep those records for another two years.
Testing rules – Require that employers provide COVID-19 testing to all employees who have come into close contact with another team member who has tested positive for the virus. Testing must be provided at no cost to the employee.
No paid leave for infected staff – Eliminate the provision for paid leave for workers who contract the coronavirus.
Handwashing and cleaning – Eliminate rules regarding handwashing and cleaning and disinfecting procedures in the workplace.
The takeaway
If you have been following Cal/OSHA’s emergency temporary standard, you should continue to follow the current requirements. The new rules simplify the emergency standard, particularly concerning the requirement that COVID-19 prevention plans can be included in your IIPP rather than in a separate document.
July 2021 – Masks for Vaccinated Staff No Longer Required

THE CAL/OSHA Standards Board has approved changes to the COVID-19 Emergency Temporary Standard that greatly loosen workplace restrictions that were implemented last year to protect California workers.
The biggest news in the changes is that workers who have been fully vaccinated are no longer required to wear face masks as protection or physically distance, regardless of the vaccination status of co-workers.
After the decision, Gov. Gavin Newsom issued an executive order enabling the revisions to take effect without the normal 10-day approval period by the state Office of Administrative Law. They came into effect when the office received the changes.
The main changes Here are the main changes affecting employers in California:
Physical distancing and barrier requirements – These are eliminated regardless of an employee’s vaccination status, except where an employer determines there is a hazard and for certain employees during major outbreaks.
Testing – Fully vaccinated employees do not need to be offered testing or be excluded from work after close contact with someone who has COVID-19, unless they have symptoms. Employees who are not fully vaccinated and exhibit COVID-19 symptoms must be offered testing by their employer.
Masks – Vaccinated workers are not required to wear face masks generally. For unvaccinated workers, masks will be required indoors or when in vehicles, with limited exceptions.
Employees are not required to wear face coverings when outdoors regardless of vaccination status, except for certain employees during outbreaks.
Document vaccination status
– Employers must document the vaccination status of fully vaccinated employees if they do not wear face coverings indoors.
No mask retaliation – Employees that choose to, are explicitly allowed to wear a face-covering without fear of retaliation from employers.
Respirator availability – Employees who are not fully vaccinated may request respirators for voluntary use from their employers at no cost and without fear of retaliation from their employers.
Businesses that need help in securing N95 respirators for unvaccinated employees can find distribution locations for state-provided N95 respirators here.
Review rules – Review the Interim Guidance for Ventilation, Filtration, and Air Quality in Indoor Environments.
Ventilation – Employers must evaluate ventilation systems to maximize outdoor air and increase filtration efficiency, and must evaluate the use of additional air cleaning systems.
What remains
Parts of the Emergency Standard still in effect include:
• Employers must maintain an effective written COVID-19 Prevention Program that includes:
» Identifying and evaluating your employees’ exposures to COVID-19 health hazards.
» Implementing effective policies and procedures to correct unsafe and unhealthy conditions.
» Allowing adequate time for handwashing and cleaning frequently touched surfaces and objects.
• Employers must provide training to employees on how COVID-19 is spread, infection-prevention techniques, and information regarding COVID-19-related benefits that affected employees may be entitled to under state or federal laws.
• Employers must bar from coming to work employees who have COVID-19 symptoms and/or are not fully vaccinated and have had close contact from the workplace if that close contact is work-related.
Cal/OSHA Rulemaking – Permanent Wildfire Safety Rules on Tap – OCTOBER 2020

AS WILDFIRES continue raging throughout California, Cal/OSHA has issued a reminder to employers that they are required to protect their outdoor workers from smoke if the Air Quality Index exceeds 150. Cal/OSHA has extended an emergency regulation it put in place in August 2019 through January 2021 as it works on a permanent regulation on wildfire smoke protection for outdoor workers in the state.
For the safety of your workers and to comply with the regulation, it’s important that you follow the regs and know when you will need to take action to protect them from outdoor smoke.
The regulation applies when the AQI for airborne particulate matter 2.5 microns (PM2.5) or smaller is 151 or greater in an area where employees are working outdoors. Here are the details:
Identification
Employers must monitor the AQI for PM2.5. You can monitor the index using the following websites:
- U.S. EPA AirNow
- U.S. Forest Service Wildland Air Quality Response Program
- California Air Resources Board
- Local air pollution control district websites or local air quality management district websites.
Training and instruction
Employers with outdoor workers need train their workers in:
- The health effects of wildfire smoke.
- Their right to obtain medical treatment without fear of reprisal.
- How they can obtain the current AQI for PM2.5.
- Actions they must take if the AQI exceeds 150 PM 2.5
Communication
Employers must implement a system for communicating wildfire smoke hazards to all affected employees, as well as a system for employees to inform the employer of smoke hazards.

The takeaway
If you have outside employees who may have to work in smoky conditions, you should stockpile a two-week supply of N-95 masks for all of them if you are unable to implement other controls to reduce their exposure.
Cal/OSHA is in the process of making the emergency rules permanent and has sent them out for public comment. We will continue monitoring the agency’s progress on the rules and update you when they have been completed.
New Law Creates COVID-19 Claim Framework – OCTOBER 2020

GOVERNOR GAVIN Newsom has signed legislation that creates a new framework for COVID-19- related workers’ compensation claims. SB 1159 replaces an executive order that Newsom made on March 18 that required all employees working outside the home who contracted COVID-19 be eligible for workers’ compensation benefits if they file a claim. The new law expands that rebuttable presumption” that a coronavirus case is work-related to front-line workers, as well as employees in workplaces that have had an outbreak of cases. The new law is retroactive to July 6, the day after Newsom’s executive order expired, and is set to expire Jan. 1, 2023. Employers with fewer than five employees are exempt under the statute.
SB 1159’s three parts
Part 1. The law codifies Newsom’s prior executive order that provided a “rebuttable presumption” that COVID-19 was contracted in the scope and course of work by employees working outside of the home who get infected.
Part 2. The law provides a rebuttable presumption that firefighters, law enforcement officers, health care workers and home care workers who contract COVID-19, contracted it in the workplace.
Part 3. The law creates a rebuttable presumption that a worker’s COVID-19 diagnosis is work-related within 14 days of a company outbreak. Under SB 1159, an outbreak is defined as when four employees test positive at a specific place of employment with 100 or fewer employees and, for larger places of employment, when 4% of the employees test positive. It’s also deemed a workplace outbreak if the employer had to shut down due to the coronavirus.
Rebutting a claim
Employers can rebut the presumption that COVID-19 was contracted at work if they have:
• Proof of measures they put in place to reduce potential transmission of COVID-19,
• Evidence of the employee’s nonoccupational risks of contracting COVID-19,
• Statements made by the employee, or
• Any other evidence normally used to dispute a work-related injury.
REPORTING REQUIREMENTS
When an employer learns of an employee testing positive, they must report to the insurer the following information within three business days:
• The date the employee tested positive.
• The address or addresses of the employee’s specific place(s) of employment during the 14-day period preceding the date of their positive test.
• The highest number of workers who reported to work in the 45-day period preceding the last day the employee worked at each specific site.
Filing False Information Can Result in a $10,000 Fine
The Rossi Law Group has the following recommendations for employers in California:
• Keep track of all locations each employee works at, the number of employees on each day at each location, as well as a log of those that test positive (including the date the specimen was collected).
• If you are aware of any staff who have tested positive between July 6 and Sept. 17, you have 30 days after Sept. 17 to report the positive test to the claims administrator.
• You must also report to the insurer positive COVID-19 results for employees that are not filing claims. In that case, you must omit personal identifying information of the employee.
• Provide any factual information to the claims administrator that could help rebut any claim of work-relatedness.
The law also has some teeth: Anyone who submits false or misleading information shall be subjected to a civil fine up to $10,000.
One last thing…
The governor also signed into law AB 685, which requires employers to report an outbreak to local public health officials. Employers must also report known cases to employees who may have been exposed to COVID-19 within one business day.
CARES ACT – New Law Helps Coronavirus-hit Employers, Workers – April 2020

THE $2 TRILLION Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act stimulus law has a number of provisions that employers and their workers need to know about and can take advantage of during this crisis.
The CARES Act aims to help workers and employers weather the outbreak by:
• Extending unemployment benefits.
• Requiring health plans to cover COVID-19-related costs.
• Providing Small Business Administration (SBA) emergency loans.
• Providing emergency loans for mid-sized and large companies.
Parts of the CARES Act will likely benefit your organization and employees in some way. Here’s what you need to know:
Extended unemployment
The CARES Act extends unemployment insurance benefits to workers, as long as they lost their jobs due to the outbreak.
Unemployment benefits under the CARES Act also apply to furloughed employees.
Workers in California will be able to collect both state unemployment and federal unemployment through the new law.
Under existing state law, workers who have lost their jobs can already receive regular unemployment benefits of between $40 and $450 per week, depending on their highest-earning quarter in a 12-month period beginning and ending before they apply for benefits with the state Employment Development Department. These benefits can last for up to 26 weeks.
The Pandemic Emergency Compensation program funded by the new law will provide an additional $600 per week on top of state unemployment benefits, through July 31.
The law extends state-level unemployment by an additional 13 weeks. For example, whereas most of California’s unemployment benefits last 26 weeks, the bill extends state benefits to 39 weeks.
The extended benefits will last through Dec. 31.
Health plan changes
Under the CARES Act, employer-sponsored group health plans must provide for covered workers – without cost-sharing or out-of-pocket expenses – the cost of COVID-19 testing, treatment and vaccinations when and if they become available.
SBA loans
In response to the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, small business owners are eligible to apply for an Economic Injury Disaster Loan advance of up to $10,000.
This advance will provide economic relief to businesses that are currently experiencing a temporary loss of revenue. Funds will be made available following a successful application. This loan advance will not have to be repaid.
This program is for any small business with fewer than 500 employees (including sole proprietorships, independent contractors and self-employed persons) as well as private non-profit organizations affected by COVID-19. You can find more information here.
And the law’s Paycheck Protection Program offers 1% interest loans to businesses with fewer than 500 workers. Borrowers who don’t lay off workers in the next eight weeks will have their loans forgiven, along with the interest. These loans are designed to provide a direct incentive for small businesses to keep their workers on the payroll. If small businesses maintain payroll through this economic crisis, some of the borrowed money via the PPP can be forgiven – the funds will be available through June 30. Act fast.
Mid-sized employers
Under the new law, the Secretary of the Treasury is authorized to implement financial assistance programs that specifically target mid-size employers with between 500 and 10,000 employees.
Loans would not have an annualized interest rate higher than 2% and principal and interest would not be due and payable for at least six months after the loan is made. But unlike loans under the PPP, these are not forgivable.
















