Worker’s Compensation – COVID-19 Prompts Rate Hike Recommendation – OCTOBER 2020

THE COVID-19 pandemic seems to have reversed years of falling workers’ compensation rates in California, as the Workers’ Compensation Insurance Rating Bureau has recommended that average benchmark rates be increased by 2.6% for 2021.
The recommendation was forwarded to the California Department of Insurance, which will schedule a hearing on the recommendation in the fall.
It should be noted that the 2.6% increase recommendation would be an average across all class codes, as the Rating Bureau plans to allocate the expected COVID-19 costs by weight across the state’s overall industrial sector. Note that even low exposure classes will be surcharged.
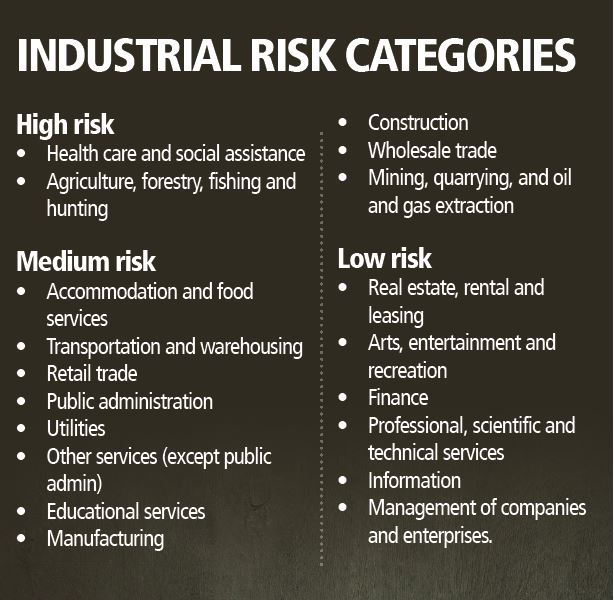
The Bureau in its recommendation aims to apply the surcharge on a weighted basis according to each class code’s share of growing COVID-19 claims costs. It is considering a tiered surcharge model based on an employer’s risk, as follows (for examples, see below):
High risk – A 12-cent surcharge per $100 of payroll.
Medium risk – A 6-cent surcharge per $100 of payroll.
Low risk – A 4-cent surcharge per $100 of payroll.
The X-factor
The Bureau’s actuarial committee noted that the pandemic does present challenges for predicting workers’ compensation costs. “The 2021 policy year will still be impacted by COVID-19, but some trends may stabilize. The challenge will be projecting exposure and claims frequency (for COVID-19 claims),” the committee wrote in a report. Actually, the overall effect of COVID-19 on rates going into 2021 was 4%, according to the Rating Bureau. Had it not included the COVID-19 surcharge, it would be asking for a 1.3% decrease in benchmark rates.
The reason is that claims costs and claims frequency have been falling and long-term claims are costing less than originally anticipated. The Bureau also forecasts that the recession caused by the pandemic will also have a profound effect on overall claims: it projects an overall 6.3% decrease in claims frequency due to slowing economic conditions.
Interestingly, COVID-19 claims are not supposed to count against employers’ experience rating and loss histories, according to new rules that took effect in May. However, the claims are having an overall effect in terms of workers’ comp benefit payments. The Bureau also has to price in the uncertainty over the future of COVID-19. Will it get worse, or will it begin to wane? Will there be a vaccine and new and improved treatment regimens that reduce mortality or decrease symptoms and hospitalizations?
It is concerned that some low-risk industries may be getting a surcharge that is still out of proportion to their actual risk, particularly with people who are working remotely. It plans to further study the issue and will likely amend the filing depending on the results.